What is ITAR Compliance and Who Needs to Comply?
Who Needs To Follow ITAR Compliance
In this ITAR Compliance Guide we’ll explore all you need to know about ITAR Compliance.
The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) is a set of US government regulations that control the export and import of defense-related articles, services, and technical data. These regulations are critical in ensuring that the US maintains its military technological superiority while preventing the unauthorized export or disclosure of sensitive information to foreign entities.
So, who needs to follow ITAR compliance? The simple answer is any individual or organization involved in the manufacture, sale, or export of defense-related items or services. This includes not only defense contractors, but also companies in related industries, such as aerospace, telecommunications, and electronics.

Under ITAR, companies must comply with a wide range of requirements, including registration with the US Department of State, implementing effective export control procedures, and ensuring that all employees receive ITAR compliance training. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in significant fines and penalties, as well as reputational damage and loss of business.
The consequences of non-compliance with ITAR can be severe, particularly for smaller businesses with limited resources. However, ITAR compliance is not just about avoiding penalties – it also helps companies establish credibility and trust with their customers, partners, and stakeholders. By following ITAR regulations, companies can demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information and upholding national security.
Types of Defense Articles
ITAR regulates the export and import of defense articles military related technologies, technical data, and defense services, which are all under its control. Defense articles refer to any item or technical data designed, developed, or modified for military, space, or intelligence applications.

The U.S. Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) administers ITAR and maintains the U.S. Munitions List (USML), which details the types of defense articles subject to ITAR controls. The USML includes 21 categories, covering a broad range of items from firearms and ammunition to military aircraft and vessels.
Examples of USML categories include:
- Firearms, Close Assault Weapons, and Combat Shotguns
- Artillery, Launchers, and Rockets
- Explosives and Energetic Materials, Propellants, Incendiary Agents, and Their Constituents
- Vessels of War and Special Naval Equipment
- Military Aircraft and Related Articles
- Military Vehicles and Related Articles
- Tanks and Military Vehicles
- Personal Protective Equipment (Body Armor, Helmets)
- Imaging and Detection Systems
- Spacecraft Systems and Associated Equipment
- Nuclear Weapons and Related Equipment
- Fire Control, Range Finder, Optical, and Guidance and Control Equipment
- Auxiliary Military Equipment
- Toxicological Agents, Including Chemical Agents, Biological Agents, and Associated Equipment
- Aircraft and Associated Equipment
- Gas Turbine Engines and Associated Equipment
- Naval Vessel Preservative Systems
- Materials, Chemicals, Microorganisms, and Toxins
- Directed Energy Weapons
- Submersible Vessels, Oceanographic and Associated Equipment
- Miscellaneous Articles
It is important to note that the above list is not exhaustive and that the DDTC has the authority to determine whether a particular item falls under ITAR controls. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to consult with ITAR compliance experts to determine whether their products or services fall under ITAR regulations.
Defense Services
Defense services involve providing assistance, like professional or technical support, for defense articles. This can happen within or outside the United States.
The defense industry includes:
- Technical assistance: instruction, skills training, and working knowledge for designing, developing, producing, processing, using, operating, overhauling, and repairing defense articles.
- Defense services also cover information sharing, such as technical data, and other non-tangible assistance related to defense articles.
Non-US persons providing defense services, even outside the United States, may face ITAR restrictions. Organizations must carefully vet and authorize defense service provisions and foreign relations according to ITAR requirements.
What Does It Mean to Be ITAR Compliant?
Being ITAR compliant means that a company or individual is following all the rules and regulations set forth by the ITAR. This includes obtaining the proper licenses and approvals for exporting defense articles, services, or technical data. It also involves properly handling and safeguarding these items to ensure that they are not being misused or transferred to unauthorized parties.
For companies or individuals involved in manufacturing, selling, or exporting defense articles or services, complying with ITAR is crucial. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, such as hefty fines, export privilege loss, and even criminal charges.
To become ITAR compliant, companies and individuals must first understand the requirements and regulations set forth by the ITAR. This includes determining whether their products or services fall under the scope of the USML, and if so, obtaining the necessary licenses and approvals before exporting them.
Additionally, companies must implement proper safeguards to protect their products and technical data from unauthorized access or misuse. This includes having secure facilities, procedures for handling and storing sensitive information, and proper training for employees who handle these items.
Overall, being ITAR compliant is essential for any company or individual involved in the export or import of defense-related articles and services. It ensures that sensitive information and products are properly handled and safeguarded, and helps to prevent unauthorized access or transfer of these items. By following ITAR regulations, companies can avoid penalties and maintain their export privileges while also contributing to national security efforts.
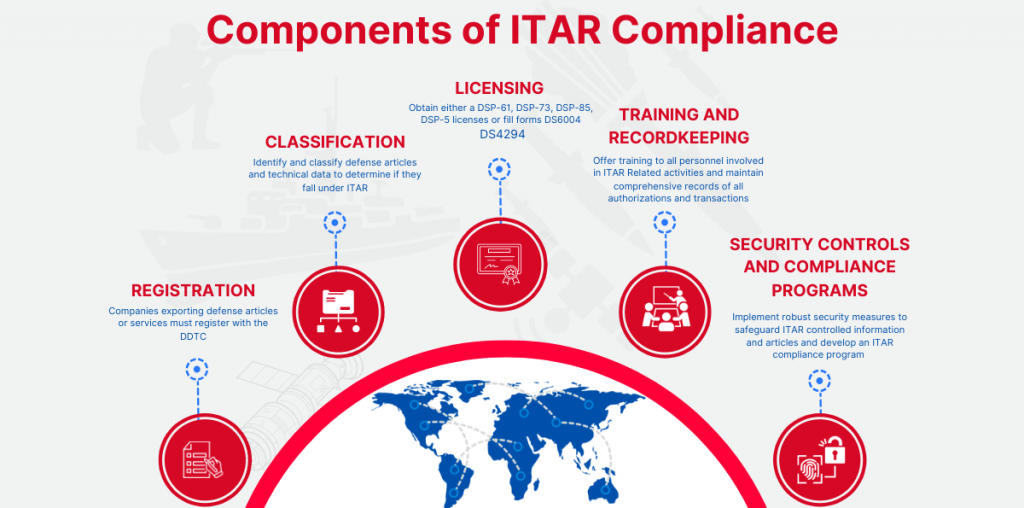
ITAR Compliance Requirements
ITAR compliance requirements are a set of regulations established by the US Department of State for the purpose of protecting national security and foreign front. The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) control the export, import, and transfer of defense-related articles and services on the United States Munitions List (USML).
ITAR compliance is mandatory for anyone involved in the manufacture, export, and transfer of defense-related articles and services listed on the USML. This includes both domestic and any foreign person or entities, as well as any person or entity that engages in the business of exporting defense articles or furnishing defense services.
To be ITAR compliant, companies must meet a variety of requirements, including:
- Registration: All companies that engage in the business of exporting defense articles or services must register with the US Department of State’s Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC). This includes manufacturers, exporters, and brokers.
- Licensing: Companies must obtain a license from the DDTC before exporting defense articles or services listed on the USML. The licensing process requires companies to provide detailed information about the article or service, the end-user, and the intended end-use.
- Recordkeeping: ITAR regulations require companies to maintain detailed records of all defense articles and services exported or manufactured. These records must include information on the type and quantity of articles or services, the end-user, and the intended end-use.
- Training: ITAR regulations require companies to provide training to employees involved in the manufacture, export, or transfer of defense articles and services. This training must cover topics such as ITAR regulations, licensing requirements, recordkeeping, and compliance.
- Compliance Programs: Companies must establish compliance programs that include policies, procedures, and controls to ensure that all activities related to the manufacture, export, and transfer of defense articles and services are in compliance with ITAR regulations.
Failure to comply with ITAR regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines, imprisonment, and loss of export privileges. Therefore, it is essential for companies involved in the manufacture, export, or transfer of defense-related articles and services to understand and adhere to all ITAR compliance requirements.
2020 ITAR Amendment
On March 9, 2020, the DDTC published a significant ITAR amendment, known as ITAR Final Rule 2018-027. It became effective on March 25, 2020. The amendment added a definition for activities excluded from ITAR controls. It clarified “technical data,” “required,” and “access” definitions and changed registration rules for brokers and manufacturers. It removed the need for certain Canadian and British dual nationals to get ITAR licenses. It revised the exemption for transfers to US persons abroad and created an exception for foreign dual nationals’ information release.
The amendment also revised licensing and agreement rules for defense services, technical data, and software. It clarified requirements for critical military technology licenses and added guidance on defense services agreements. The 2020 ITAR amendment aimed to modernize and streamline ITAR regulations while protecting national security. Organizations in defense-related activities should stay updated on ITAR requirements and amendments to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
What Data Does Not Fall Under ITAR?
Publicly available information is usually not ITAR-controlled. This includes published information from books, periodicals, or the internet, and public domain data or government-released information.
Fundamental research, conducted at US higher learning institutions, is also not under ITAR control. However, technology or technical data from this research may be subject to ITAR or other export control regimes if designed or modified for military use.
Data controlled by other regulations, like the Export Administration Regulations (EAR), may not fall under ITAR control. EAR controls dual-use items with civilian and military applications, and some items under ITAR regulations may also be controlled by EAR.
What Are ITAR Articles, Services and Technical Data?
ITAR Articles include physical items such as equipment, parts, and components, which are specifically designed or modified for military use, including defense articles and defense services. * ITAR articles also includes any technical data or software directly related to these defense articles.
ITAR Technical Data refers to information, including blueprints, plans, diagrams, models, formulae, tables, engineering designs, specifications, manuals, and instructions, that is required for the design, development, production, manufacture, assembly, operation, repair, testing, maintenance, or modification of defense articles.
ITAR Services include services related to defense articles, other defense and military technologies guidance equipment materials such as installation, maintenance, training, repair, and other support services. Providing these services to foreign nationals or entities requires ITAR compliance.
It is crucial to understand what falls under ITAR regulation to avoid severe legal consequences. Failure to comply with ITAR regulations can result in significant fines, loss of export privileges, and even criminal charges. Therefore, it is important to consult with a qualified ITAR consultant to ensure compliance with all applicable ITAR regulations.
Understanding ITAR Technical Data Compliance
ITAR regulates technical data, which includes information about defense articles like blueprints, plans, and documentation. Companies handling technical data must follow ITAR rules.
To remain ITAR compliant, companies must limit technical data access to US persons. Non-US persons need US government authorization, usually through licensing and certification.
To follow ITAR rules, companies need strong data security measures. They must use access controls, like firewalls and user authentication, to protect data and allow only authorized access. Companies also need systems to detect unauthorized access attempts.
When transferring technical data outside the US, companies must meet ITAR requirements. This includes getting licenses or authorizations from the US government and using secure communication channels.
Companies must train their staff on ITAR rules and internal procedures to ensure compliance. Proper training helps personnel handle technical data securely and in line with regulations.
In summary, ITAR compliance needs strong data security, access control, and employee training to ensure secure and lawful handling of technical data.
Secure Sharing of ITAR Data With End-to-End Encryption
ITAR compliance is critical for companies that deal with defense-related products and services. One of the key components of ITAR compliance is the protection of technical data related to defense articles and services. However, many companies need to share this data with their partners, vendors, and other stakeholders in the course of doing business. To ensure secure sharing of ITAR data, end-to-end encryption is essential.
End-to-end encryption is a method of securing communication where only the communicating users can read the messages. This means that even the service provider cannot read the messages being exchanged. End-to-end encryption ensures that the data remains private and secure at all times, even if it is intercepted by a third party.
When sharing ITAR data, it is important to ensure that the encryption method used is ITAR compliant. The ITAR regulations require that any encryption used to protect technical data must meet specific requirements.
These requirements include:
- The encryption must be secure and strong enough to prevent unauthorized access.
- The encryption must be validated and approved by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
- The encryption key must be protected and kept secret.
- The encryption must be able to protect the data from interception, modification, or deletion.
By using end-to-end encryption that meets these requirements, companies can ensure that their ITAR data is protected while being shared with authorized parties. It is also important to ensure that the recipient of the data is authorized to receive it and has the proper security measures in place to protect it.
ITAR Regulations
ITAR regulations apply to many defense-related items like military hardware, software, and technology. They cover items designed, developed, or modified for military use, as well as services involving these items, such as training, repair, or maintenance.
ITAR rules include not only physical items but also technical data related to defense articles. Technical data involves information needed for designing, developing, producing, using, maintaining, or repairing defense articles.
Exporting and importing defense-related items under ITAR requires a license from the U.S. Department of State. Obtaining a license is complex and demands a thorough understanding of ITAR regulations.
Government Contractors Need an ITAR Compliance Plan
Government contractors who deal with defense articles and services need to have an ITAR compliance plan in place. ITAR, or the International Traffic in Arms Regulations, is a set of regulations that control the export and import of defense-related articles, services, and technical data. The United States government requires these regulations to be followed to protect national security interests.
ITAR compliance plans are essential for government contractors because noncompliance can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. The regulations can be complex and change frequently, so contractors need to stay up-to-date on the latest requirements to avoid violations.
An effective ITAR compliance plan should include the following components:
- Comprehensive understanding of the ITAR regulations and how they apply to the contractor’s operations.
- Implementation of proper procedures to ensure compliance with the regulations.
- Regular training for employees on ITAR regulations and compliance procedures.
- Thorough record-keeping to document compliance efforts.
- Periodic internal audits to assess compliance and identify areas for improvement.
- Use of secure communication and data storage methods to prevent unauthorized access to ITAR-related information.
- Contractual obligations to ensure that subcontractors and vendors also comply with ITAR regulations.
By having an effective ITAR compliance plan in place, government contractors can avoid the severe consequences of noncompliance and demonstrate their commitment to national security.
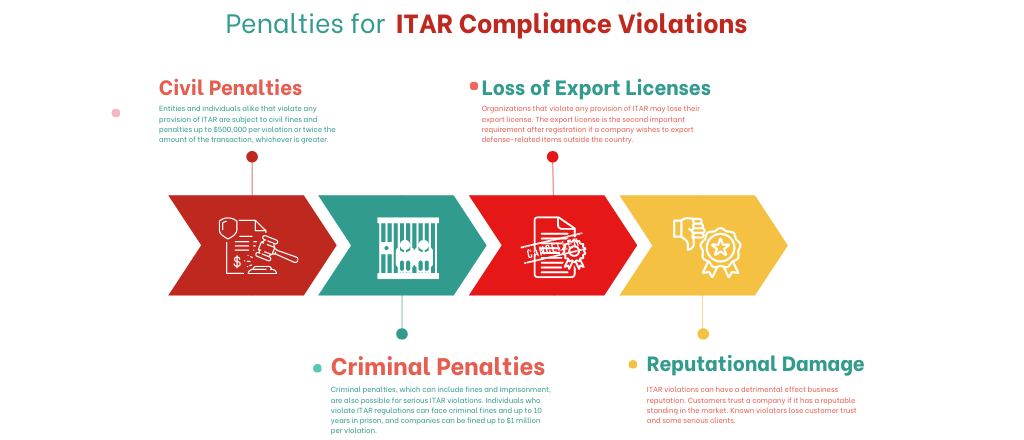
Penalties for ITAR Compliance Violations
Penalties for ITAR compliance violations can be severe, including civil fines, criminal charges, and even imprisonment. The U.S. Department of State’s Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC) enforces ITAR regulations, and they have the power to investigate violation criminal fines, and take action against any violation.
Civil fines and penalties for ITAR violations can reach up to $500,000 per violation or twice the amount of the transaction, whichever is greater. Criminal penalties, which can include fines and imprisonment, are also possible for serious ITAR violations. Individuals who violate ITAR regulations can face criminal fines and up to 10 years in prison, and companies can be fined up to $1 million per violation.
In addition to the financial and legal consequences of ITAR violations, companies that violate ITAR regulations may also face reputational damage and loss of business. Government agencies and defense contractors may be hesitant to work with companies that have a history of ITAR violations.
To avoid these penalties, it is important for companies that deal with defense-related products and services to establish an ITAR compliance program that includes policies, procedures, training, and ongoing monitoring to ensure that all activities are in compliance with ITAR regulations.
Who Needs to Be ITAR Compliant
Anyone involved in the manufacture temporary import control of, export, and import of defense articles, defense services, or technical data is subject to ITAR regulations.
This includes U.S. companies, foreign companies, and individuals. ITAR compliance is particularly important for government contractors, as they are often involved in the manufacture, supply chain and export of defense articles and technical data. In addition, anyone who works with sensitive military technology or data must also comply with ITAR regulations.
Other entities that may need to be ITAR compliant include:
- Manufacturers of defense articles and defense services
- Exporters of defense articles and defense services
- Brokers of defense articles and defense services
- Researchers working on sensitive military technology or data
- Contractors who work on U.S. military bases
- U.S. citizens and residents working abroad in defense-related roles
It is important to note that ITAR regulations apply not only to the export of physical items, but also to the transfer of related technical data, and services. This means that even if an item is not physically leaving the country, the transfer of technical data and defense related to that item is still subject to ITAR regulations.
Failure to comply with ITAR regulations can result in severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment. Therefore, it is essential for companies and individuals who are involved in the manufacture, export, and import of defense articles, defense services, or technical data to understand and comply with ITAR regulations.
How do I know if I am ITAR compliant?
To know if your business or organization is ITAR compliant, you need to perform an assessment of your operations, products, and services.
Here are some steps to take:
- Identify if your company manufactures, exports, or deals with defense articles or defense services, as defined by the ITAR regulations.
- Determine if you have access to technical data related to defense articles or defense services, or if you provide IT services that support these activities.
- Review your internal processes, procedures, and policies to ensure that they align with the ITAR and export regulations.
- Assess your workforce to ensure that they are properly trained and knowledgeable about the ITAR requirements.
- Verify that your IT infrastructure is secure, and that you have appropriate controls in place to protect sensitive technical data.
- If you are unsure about your compliance status, consider hiring a third-party consultant or legal counsel who specializes in ITAR compliance to review your operations and provide guidance.
By taking these steps, you can ensure that your company is ITAR compliant and avoid potential penalties and legal ramifications for noncompliance.
Which Countries are ITAR Restricted?
The U.S. government’s Department of State, Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC), determines ITAR-restricted countries. The periodically updated list includes countries posing a risk to U.S. national security or foreign policy interests.
As of September 2022, the following countries are considered ITAR-restricted in line with 22 CFR 126.1(d)(1): Belarus, Burma, China, Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Syria, and Venezuela.
It is important to note that this list is subject to change, and individuals and organizations should consult with the DDTC or an ITAR compliance expert to ensure they are aware of any updates or changes to the list.
ITAR compliance checklist for protecting your data and defense services
An ITAR compliance checklist can help ensure that your organization is taking all necessary steps to protect your data and avoid penalties for noncompliance.
Here are some key items to include in your ITAR compliance checklist:
- Identify all ITAR-controlled technical data, articles, and services in your organization.
- Implement appropriate physical and digital security measures to protect ITAR-controlled data.
- Control access to ITAR-controlled data by only providing access to authorized personnel.
- Keep records of all ITAR-controlled technical data, articles, and services, including any transfers of data to other organizations.
- Implement a compliance program to ensure that all employees are aware of ITAR regulations and are following the necessary procedures.
- Train all employees who work with ITAR-controlled data on the regulations and procedures related to ITAR compliance.
- Conduct regular audits and assessments to ensure that your organization is maintaining compliance with ITAR regulations.
- Have a plan in place for responding to any potential violations of ITAR regulations, including reporting the violation to the appropriate authorities.
By following these key steps, you can help ensure that your organization is fully compliant with ITAR regulations and is taking all necessary steps to protect your sensitive data.
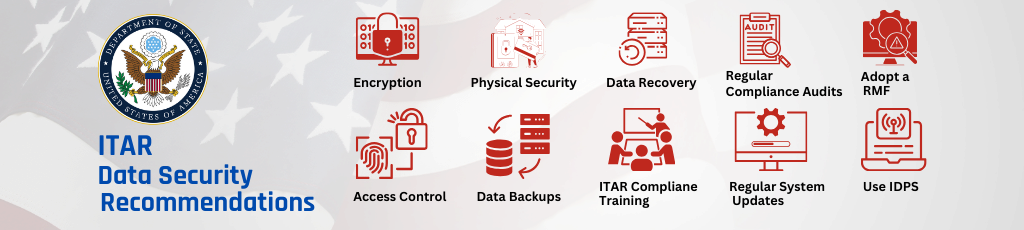
ITAR Data Security Recommendations
One of the key requirements of ITAR compliance programs is the protection of sensitive data. In this article, we will discuss some of the recommended data security measures that organizations can implement to ensure compliance with ITAR regulations.
- Access Control: ITAR data should be accessible only to authorized personnel who have a need to know. Access control measures such as password protection, two-factor authentication, and biometric authentication can help ensure that only authorized personnel can access ITAR data.
- Encryption: Encrypt ITAR data both in transit and at rest. Using end-to-end encryption secures data from the moment it leaves the sender until the intended recipient receives it. Encryption helps prevent unauthorized access to ITAR data and protects the data in case of a breach.
- Physical Security: Physical security measures such as locked cabinets, access controls, and security cameras can help protect physical ITAR data from theft or unauthorized access. Secure storage of ITAR data is critical to ensuring compliance with ITAR regulations.
- Data Backup and Recovery: ITAR data should be regularly backed up and stored securely offsite. Regular data backups can help ensure that data is not lost due to hardware failures or natural disasters. In addition, having a disaster recovery plan can help organizations recover from data breaches or other catastrophic events.
- ITAR Compliance Training: Organizations should provide ITAR compliance training to all employees who handle ITAR data. This training should include information on ITAR regulations, how to handle ITAR data, and what to do in the event of a data breach. Ongoing training can help ensure that employees are aware of their responsibilities and are following best practices for data security.
- Regular ITAR Compliance Audits: Organizations should conduct regular audits to ensure that ITAR data is being handled according to ITAR regulations. These audits should include an assessment of data security measures, access controls, and data backup procedures. Regular audits can help organizations identify vulnerabilities and take corrective action to ensure compliance with ITAR regulations.
What Are The Most Common ITAR Violations?
There are several common ITAR violations that can result in penalties and legal action.
Some of the most frequent ITAR violations include:
- Unauthorized access: Allowing individuals who are not authorized to access ITAR-controlled information or technology is a violation. This can include sharing sensitive information with unauthorized employees or contractors.
- Failure to register: Companies that work with ITAR-controlled technology must register with the US Department of State’s Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC). Failure to register can result in penalties and legal action.
- Export violations: Exporting ITAR-controlled technology without a license or in violation of licensing requirements is a serious violation. This includes physical exports, as well as electronic exports such as sending files or data to foreign countries.
- Failure to maintain records: Companies must maintain accurate and complete records of all ITAR-controlled technology transactions, including exports and retransfers. Failure to maintain these records can result in penalties and legal action.
- Failure to provide required disclosures: Companies that work with ITAR-controlled technology must disclose certain information to the US government, including information about any foreign persons or entities that will have access to the technology. Failure to provide these disclosures can result in penalties and legal action.
It is important for companies to have a comprehensive ITAR compliance program in place to avoid these common violations and ensure they are meeting all ITAR requirements.
Share in Social Media
See More Case Studies

Securing Defense Contracts: A DFARS 252.204-7012 Compliance Case Study
Discover how Cleared Systems helped a Federal Contractor successfully achieve DFARS 252.204-7012 compliance by strengthening its cybersecurity posture, giving it a competitive edge when bidding for DoD Contracts.

What is GCC High? For ITAR & CMMC 2.0
Microsoft 365 Government Community Cloud (GCC) High is a specialized cloud solution tailored for U.S. federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations, as well as for contractors who hold or process data subject to specific security regulations. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, and differences between Microsoft 365 GCC High and other Office 365 offerings.
Is AutoCAD ITAR Compliant? A Comprehensive Guide for Defense Manufacturers
Defense contractors and manufacturers working with sensitive military technologies face a critical question when selecting computer-aided design software: Is AutoCAD ITAR compliant? This question becomes

How to Get Help in Windows: Guide to Security and Compliance Support
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring your computer systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations is essential for both businesses and individuals. Windows, as one

Microsoft Copilot for GCC High: Enhancing Security and Compliance
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, organizations that handle sensitive data, particularly those in government sectors or defense contractors, face growing pressure to maintain strict security
Partner with Us for Compliance & Protection
We’re happy to answer any questions you may have and help you determine which of our services best fit your needs.
Your benefits:
- Client-oriented
- Security
- Compliance
- Peace of mind
- Efficiency
- Trust
What happens next?
Schedule an initial meeting
Arrange a discovery and assessment call
Tailor a proposal and solution



