Which Microsoft Cloud Version Meets DFARS, NIST and ITAR Security Requirements?
As technology evolves, the need for robust cybersecurity measures increases. Organizations that work with sensitive data, such as the government, the military, and defense contractors, have specific security compliance requirements they need to meet. In the United States, the most common requirements are defined by three sets of regulations: DFARS, NIST, and ITAR. When choosing a cloud provider, it’s essential to understand which version of the cloud meets these requirements. In this article, we will compare Microsoft Commercial, Microsoft GCC, and Microsoft GCC High.
DFARS, NIST, and ITAR Explained
DFARS (Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation Supplement) is a comprehensive set of guidelines that stipulates the cybersecurity requirements for defense contractors. While it is fundamentally based on the guidelines provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), DFARS goes a step further by incorporating specific requirements for Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) and Covered Defense Information (CDI). These additional stipulations ensure that sensitive information pertaining to national defense is adequately protected.
NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology), on the other hand, provides a universally applicable framework that outlines guidelines, standards, and best practices for managing and enhancing information security. This framework is leveraged by a wide range of entities, including government agencies and private companies, to bolster their cybersecurity measures and protect their digital assets.
ITAR (International Traffic in Arms Regulations) is a distinct set of rules that governs the export and import of defense-related goods and services. Companies that deal with military technologies – encompassing hardware, software, and data – are required to comply with ITAR. This ensures that critical military technologies are handled responsibly and do not fall into the wrong hands.
Comparing Microsoft Cloud Versions
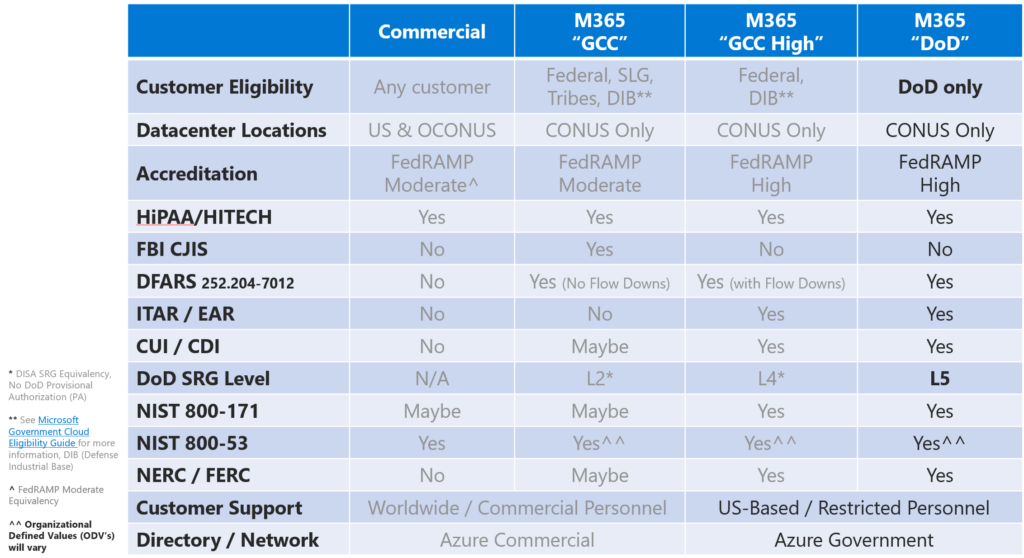
Improve “Microsoft offers three versions of its cloud services: Commercial, Government Community Cloud (GCC), and Government Community Cloud High (GCC High). Here’s how they compare in terms of DFARS, NIST, and ITAR compliance.
Microsoft Commercial
Microsoft Commercial is the standard cloud service offered by Microsoft to all its customers, including government agencies and defense contractors. It meets many of the NIST guidelines, but it does not have specific features for DFARS or ITAR compliance. Therefore, using Microsoft Commercial alone may not be sufficient for DFARS, NIST, and ITAR compliance. However, it can be used as part of a multi-cloud approach where other clouds are used to meet the specific compliance requirements.
Microsoft GCC
Microsoft GCC is a cloud service designed for U.S. government agencies, including state and local government entities. It is built on top of the Commercial cloud, but it provides additional security features that meet the requirements of DFARS and ITAR. The service is isolated from the commercial cloud, and data is stored in data centers located within the United States. It also meets many of the NIST guidelines.
Microsoft GCC High
Microsoft GCC High is a cloud service designed for the Department of Defense and other government agencies that require the highest level of security. It meets all the requirements of DFARS, NIST, and ITAR. It provides the highest level of security controls and is designed to protect sensitive information, including classified information.
Microsoft 365 Government – DoD
Microsoft 365 Government – DoD is a cloud service tailored for the US Department of Defense and contractors dealing with DoD controlled unclassified information (CUI) or subject to ITAR. It complies with US public sector certifications and provides high-level security controls. It meets NIST 800-800-53 controls and DoD Cloud Computing Security Requirements Guide (SRG) up to Impact Level 5 (L5). Eligibility validation is required to use this service.
Conclusion
Choosing the right version of Microsoft cloud services depends on the level of security and compliance requirements of your organization. Microsoft Commercial may be sufficient for some organizations, but those that handle sensitive data and work with the government or defense contractors should consider Microsoft GCC or Microsoft GCC High. While Microsoft GCC meets the requirements for DFARS and ITAR, Microsoft GCC High provides the highest level of security controls and is designed to protect sensitive information, including classified information. It is important to note that all versions of Microsoft cloud services meet many of the NIST guidelines. Please note: Microsoft GCC High has higher licensing requirements than Microsoft Commercial and Microsoft GCC.
In conclusion, it’s essential to understand the specific compliance requirements of your organization and choose the version of Microsoft cloud services that best meets those requirements. Whether it’s Microsoft Commercial, Microsoft GCC, or Microsoft GCC High, Microsoft provides robust cloud services that can help keep your data secure.
Share in Social Media
See More Case Studies

Securing Defense Contracts: A DFARS 252.204-7012 Compliance Case Study
Discover how Cleared Systems helped a Federal Contractor successfully achieve DFARS 252.204-7012 compliance by strengthening its cybersecurity posture, giving it a competitive edge when bidding for DoD Contracts.

What is GCC High? For ITAR & CMMC 2.0
Microsoft 365 Government Community Cloud (GCC) High is a specialized cloud solution tailored for U.S. federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations, as well as for contractors who hold or process data subject to specific security regulations. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, and differences between Microsoft 365 GCC High and other Office 365 offerings.
Is AutoCAD ITAR Compliant? A Comprehensive Guide for Defense Manufacturers
Defense contractors and manufacturers working with sensitive military technologies face a critical question when selecting computer-aided design software: Is AutoCAD ITAR compliant? This question becomes

How to Get Help in Windows: Guide to Security and Compliance Support
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring your computer systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations is essential for both businesses and individuals. Windows, as one

Microsoft Copilot for GCC High: Enhancing Security and Compliance
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, organizations that handle sensitive data, particularly those in government sectors or defense contractors, face growing pressure to maintain strict security
Partner with Us for Compliance & Protection
We’re happy to answer any questions you may have and help you determine which of our services best fit your needs.
Your benefits:
- Client-oriented
- Security
- Compliance
- Peace of mind
- Efficiency
- Trust
What happens next?
Schedule an initial meeting
Arrange a discovery and assessment call
Tailor a proposal and solution
