What You Should Know About CMMC 2.0 Level 2
The Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) was developed by the United States Department of Defense (DoD) to ensure that companies that work with the government have adequate cybersecurity measures in place. The CMMC model has five levels of certification, with level 2 being a higher level of certification than level 1. In this article, we will discuss the basics of CMMC 2.0 Level 2 and what you need to know to achieve compliance.
What is CMMC Level 2?
CMMC Level 2 is the second level of certification in the CMMC model. It is designed for companies that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). CUI is unclassified information that requires safeguarding or dissemination controls required by law, regulation, or government-wide policy. CMMC Level 2 requires the implementation of the cybersecurity practices described below. These practices are based on the requirements of the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-171.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Security Requirements
Under the rule, security requirements for CMMC Level 2 mirror the practices in NIST SP 800-171 Rev 2. Therefore, contractors and subcontractors must implement all applicable SP 800-171 Rev. 2’s requirements. The OSA also must implement the specific requirements of DFARS 252.204.7012. However, there are two avenues to verify that a contractor has implemented the CMMC 2.0 Level 2 requirements. Henceforth, program contracts will either have a CMMC Level 2 Certification Assessment or CMMC Level 2 Self-assessment requirement. CMMC Level 2 also allows for the use of POA&M for select security requirements. However, they MUST be closed out within 180 days. Since CMMC Level 2 is based on NIST SP 800-171, it is worth noting that security requirements may change in the future as the Special Publication undergoes revision. This means that when NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 3 comes into effect, the security requirements for CMMC Level 2 may change considerably.
Scoping
Before embarking on the CMMC Level 2 Assessment, the OSA must specify the Assessment Scope. What is the CUI footprint? Which Assets are in scope and which are not? Proper scoping has an impact on the assessment costs and time. CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Assessment Scope involves asset categories and requirements detailed in the table below. An OSA must have a Level 2 Final Certification Assessment if it uses an ESP other than a CSP. However, if the ESP is external to the OSA, the organization must list the security requirements it has implemented on its SSP. This shows the connection between the ESP and OSA’s in-scope environment. To be considered an ESP within CMMC, Security Protection Data or CUI should be processed, stored, or transmitted on the ESP assets.
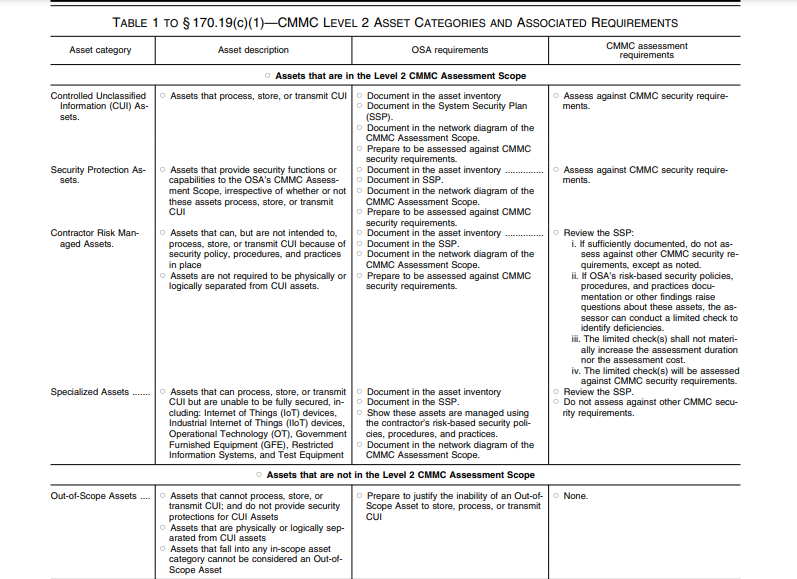
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Self-Assessment
CMMC Level 2 allows for Self-Assessments and Certification Assessments. However, the OSA must fulfill some preconditions to comply with CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessment stipulations. It must meet all the CMMC Level 1 Self-Assessment and Affirmation requirements detailed in § 170.15 for the same CMMC Assessment Scope.
Self-Assessment Procedures
Such an organization should then complete a self-assessment for all security practices in NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 2 with a MET result. Additionally, the Self-Assessment should;
- Be conducted per NIST SP 800-171A and CMMC Level 2 Scoping requirements.
- Be scored in line with CMMC Level 2 scoring methodology; and
- If the assessment results in a POA&M, the OSA must perform a POA&M closeout assessment within 180 days after remediating all the remaining requirements.
After completing the Self-Assessment, the OSA should submit the results to the Supplier Performance Risk System (SPRS). These results should include the CMMC level, assessment date, assessment scope, CAGE code(s), self-assessment score, and, where applicable, POA&M usage and compliance status. However, the OSA has to conduct a triennial CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessment to maintain compliance. The OSA must submit affirmations with each evaluation and annually for all CMMC Level 2 Self-Evaluations.
Conditional Self-Assessment
If the Self-Assessment results in a POA&M that meets all Level 2 POA&M requirements, the OSA has achieved a Conditional Self-Assessment. However, the OSA must still perform a POA&M closeout and submit the compliance results to SPRS. This has to be done within 180 days of the initial Self-Assessment. Failure to meet this deadline results in the expiration of the Conditional Level 2 Self-Assessment status and ineligibility for further awards requiring CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessment or higher.
Self-Assessment of Cloud Service Provider
To process, store, or transmit CUI, an OSA may use a FedRAMP Moderate or higher cloud in fulfillment of a contract or subcontract that has a CMMC Level 2 requirement if;
- The CSP’s service or product offering is FedRAMP-authorized at a Moderate or higher baseline.
- The CSP’s service or product offering isn’t FedRAMP authorized at a Moderate or higher baseline but meets security requirements equivalent to those established by the FedRAMP Moderate (or higher) baseline.
- The Assessment Scope includes the OSA’s on-premises infrastructure connecting to the CSP’s product or service offering. Therefore, the security requirements from the CRM must be documented or referred to in the OSA’s SSP.
Final Self-Assessment and CMMC Status Revocation
After Implementing all the security requirements and closing out the POA&M, the OSA achieves Level 2 Final Self-Assessment Compliance for the assets in the CMMC Assessment Scope. The CMMC PMO reserves the right to revoke the validity status of a CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Self-Assessment. This can happen if the PMO determines that an organization hasn’t achieved or maintained the provisions of CMMC Levels 1 and 2. Whenever this happens, contractual remedies apply. The OSA becomes ineligible for further awards with a CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessment or higher. The OSA has to achieve a valid level 2 Self-Assessment to bid for contracts again.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Certification Assessment and Affirmation
Unlike CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessments, Certification Assessments are conducted by an authorized or accredited C3PAO. However, the OSC must ensure it meets the Certification Assessment requirements. Fortunately, addressing CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Certification Assessment requirements in § 170.17(a)(1) and (2) satisfies the CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessment requirements for the same Assessment Scope. To begin with, the OSC must implement and achieve all the security requirements in this table with a MET result.
Certification Assessment Procedures
After an organization implements the security requirements for CMMC Level 2, it may either achieve a Conditional or Final Certification through a CMMC Level 2 Certification Assessment by a C3PAO. The C3PAO should;
- Conduct the Certification Assessment per NIST SP 800-171A and CMMC Level 2 Scoping requirements.
- Score the Certification Assessment in line with CMMC Level 2 scoring methodology; and
- Communicate the final results to the OSC through the CMMC Assessment Findings Report.
- Submit the assessment results into eMASS, that automatically transmits them to SPRS.
To continue bidding for contracts, the OSC must maintain compliance with the CMMC. Additionally, Level 2 Certification Assessments are performed triennially. However, the OSC must send affirmations after each assessment is completed and annually after that. These affirmations attest that the OSC complies with the CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Certification’s security requirements.
Uploads to the eMASS
For a CMMC Level 2 Certification Assessment, the CMMC instantiation of eMASS shall, at least, include the following information:
- Name and unique identifier of the C3PAO
- Date and level of the assessment
- Assessor Details like name and business contact information
- All industry CAGE codes associated with the information systems addressed by the CMMC Assessment Scope.
- The name, date, and version of the SSP.
- Title 32 program rule (32 CFR part 170) at the time of assessment.
- Certification date.
- Assessment result for each requirement objective.
- POA&M usage and compliance, as applicable.
- List of the artifact names, the return values of the hashing algorithm, and the hashing algorithm used.
Conditional Vs. Final Certification Assessment
A conditional Certification assessment is awarded to an OSC if the assessment’s completion results in the creation of a POA&M. However, the POA&M must adhere to all the CMMC 2.0 Level 2 POA&M requirements; otherwise, the OSC won’t be granted Conditional Certification. On the other hand, if the OSC has implemented all the security requirements for the information systems in the CMMC Assessment Scope and has closed out all POA&M, it may be granted a Final Certification Assessment. Like in Self-Assessment, The OSC is required under the rule to implement the deficient Level 2 requirements and close out the POA&M within 180 days after the initial assessment.
After addressing the deficiencies, the OSC should contact the C3PAO for a POA&M closeout assessment. The Assessor Organization submits the results of the closeout assessment into the CMMC Instance of the eMASS that automatically transmits them to SPRS. Failure to close out the POA&M within 180 days results in the expiration of the CMMC Level 2 Conditional Certification Assessment. Standard contractual remedies kick in if Conditional CMMC Level 2 Certification expires within the contract performance period. As a result, the OSC becomes ineligible for additional solicitations with a CMMC Level 2 Certification Assessment or higher, particularly for the assets within the Assessment Scope.
Security Requirement Re-evaluation
A security requirement with a result NOT MET can be reassessed during the assessment period and for 10 business days afterward, although under certain conditions. These include:
- Additional evidence showing that the security requirement has been MET is adduced;
- The security requirement can’t limit or change other MET requirements, and
- The non-delivery of the CMMC Assessment Findings Report.
CMMC Status Revocation
If it is determined that an organization hasn’t achieved or maintained the provisions of CMMC Levels 1 and 2, the CMMC PMO can, at their discretion, revoke the validity status of a CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Self-Assessment. Whenever this happens, contractual remedies apply. The OSC becomes ineligible for further awards with a CMMC Level 2 Certification Assessment or higher. The OSC has to achieve a valid Level 2 Certification Assessment to bid for contracts again. It’s worth noting that a revocation of a Level 2 Certification Assessment automatically results in revocation of CMMC Level 3 Certification, if any, dependent upon that CMMC Level 2 Final Certification Assessment.
Artifact Retention
OSCs must preserve the evidence artifacts used during the Certification Assessment for the entire certification period and for a minimum of six years post-assessment. To verify the integrity of these artifacts, OSCs should apply a NIST-approved hashing algorithm to the artifact files. Subsequently, OSCs must furnish the C3PAOs with an inventory of the artifact names, the hash values generated, and the specific hashing algorithm used. This information is then uploaded to the CMMC module within the eMASS system. CMMC Level 2 Cloud Certification Assessment is similar to that used in Self-Assessment.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 POA&M Requirements
As part of the requirement CA.L2–3.12.2, an OSA is allowed to maintain a time-limited POA&M as part of operations security for CMMC 2.0 Level 2. However, an OSA can only have a POA&M if it meets the following conditions:
- Assessment Ratio: The ratio of the assessment score to the total security requirements must be at least 0.8;
- Excluded Requirements: The POA&M must not contain any of the following security requirements:
- AC.L2–3.1.20: External Connections involving CUI Data.
- AC.L2–3.1.22: Control of Public Information pertaining to CUI Data.
- PE.L2–3.10.3: Escorting Visitors within areas where CUI Data is present.
- PE.L2–3.10.4: Maintenance of Physical Access Logs for CUI Data.
- PE.L2–3.10.5: Management of Physical Access to CUI Data.
- POA&M Point Limit: Security requirements listed in the POA&M should not exceed a point value of 1, according to the CMMC Scoring Methodology, except for SC.L2–3.13.11 regarding CUI Encryption, which may be included if it scores 1 or 3.
How to achieve compliance with CMMC Level 2?
To achieve compliance with CMMC Level 2, companies must implement all the NIST SP 800-171 practices for the purposes of a Self-Assessment. However, an OSC must complete and achieve a MET result for all security requirements specified in table 1 to § 170.14(c)(4) CMMC Level 3 Requirements for the purposes of CMMC Level 2 Certification Assessment. The following are the steps that companies can take to achieve compliance:
Scoping
The first step towards achieving CMMC Level 2 compliance is to identify the information systems in your organization that process, store, or transmit CUI. This includes not only your organization’s internal information systems but also any Cloud Service Providers (CSPs) and External Service Providers (ESPs) that you use. The scoping should be done in accordance with the requirements in § 170.19(c). It’s important to remember that the scope of compliance extends to all systems that process, store, or transmit Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI).
Conduct Gap Analysis
Once the scope is defined, the next step is to conduct a gap analysis. This involves comparing your organization’s current cybersecurity posture with the requirements of CMMC 2.0 Level 2. The goal is to identify any gaps or deficiencies that need to be addressed. This step is crucial for understanding the amount of work that needs to be done to achieve compliance.
Establish System Security Plan (SSP)
With the gaps identified, the next step is to create a System Security Plan (SSP). This is a comprehensive document that outlines your organization’s security objectives and the measures you plan to implement to meet the CMMC 2.0 Level 2 security requirements. The SSP is a requirement of NIST SP 800-171 Rev. 2 practice 3.12.4. It serves as a roadmap for your organization’s journey towards compliance.
Undertake Gap Remediation
After the SSP is established, the next step is to undertake gap remediation. This involves implementing the necessary Level 2 security requirements specified by the CMMC framework to address the identified gaps. It’s important to note that this should be an ongoing process, as new gaps may be identified over time.
Undergo CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Self-Assessment
Once the gaps have been addressed, the next step is to perform a self-assessment. This involves determining your organization’s current compliance with the required CMMC 2.0 Level 2 security requirements using the procedure in § 170.16(c) and the scoring methodology detailed in § 170.24 of the proposed rule. The self-assessment is a critical step in validating that the gap remediation efforts have been successful.
Prepare Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M)
After the self-assessment, the next step is to develop a Plan of Action and Milestones (POA&M). This is a detailed roadmap that outlines specific actions, responsible parties, timelines, and milestones to address any remaining risks and deficiencies. The POA&M must be in accordance with the CMMC POA&M requirements listed in § 170.21(2) of the proposed rule.
POA&M Close Out
The next step is to address the deficiencies found during the CMMC Level 2 Self-Assessment that are listed in the POA&M document. This involves implementing the necessary measures to close out each item on the POA&M.
CMMC 2.0 Level 2 Certification Assessment
After the POA&M close out, the next step is to work with a CMMC Third Party Assessor Organization (C3PAO) to conduct an official § 170.17 Certification Assessment. This is a formal evaluation of your organization’s compliance with the CMMC Level 2 requirements.
POA&M Closeout Or Assessment Finding Upload
If the Certification Assessment results in a POA&M, the next step is to address the deficiencies within the stipulated time. If there are no deficiencies, the C3PAO will upload the results into the CMMC Instance of the eMASS, which automatically transmits them to the SPRS, placing you in a clear path to certification.
Obtain Final Certification Assessment
After addressing the deficiencies and uploading the results to the SPRS, your organization receives the Final Certification Assessment. It’s important to note that the certification has a validity of three years, but the CMMC PMO may revoke it if it is determined that your organization hasn’t achieved or maintained the provisions of CMMC Levels 1 and 2
Continous Monitoring
Finally, it’s crucial to continuously monitor your information systems to ensure that you remain compliant with CMMC 2.0 Level 2 security requirements. If you fail to maintain compliance, you risk having your certification revoke. Additionally, you are required to submit annual affirmations attesting that your organization is CMMC Level 2 compliant. These affirmations must be submitted in line with the requirements set out in § 170.22(a), § 170.22(b)(2), and (3).
Conclusion
CMMC Level 2 is a higher level of certification than Level 1, and it is designed for companies that handle Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Compliance with CMMC Level 2 requires the implementation of 55 cybersecurity practices. Companies can achieve compliance by identifying the scope of the system that requires compliance, performing a self-assessment, identifying any gaps and deficiencies, developing a plan to address them, implementing the plan, obtaining a third-party assessment, and uploading the assessment results to the DoD’s SPRS. Achieving compliance with CMMC 2.0 Level 2 is a significant step towards ensuring the security of the nation’s critical infrastructure and protecting sensitive government information.
Share in Social Media
See More Case Studies

Securing Defense Contracts: A DFARS 252.204-7012 Compliance Case Study
Discover how Cleared Systems helped a Federal Contractor successfully achieve DFARS 252.204-7012 compliance by strengthening its cybersecurity posture, giving it a competitive edge when bidding for DoD Contracts.

What is GCC High? For ITAR & CMMC 2.0
Microsoft 365 Government Community Cloud (GCC) High is a specialized cloud solution tailored for U.S. federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations, as well as for contractors who hold or process data subject to specific security regulations. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, and differences between Microsoft 365 GCC High and other Office 365 offerings.
Is AutoCAD ITAR Compliant? A Comprehensive Guide for Defense Manufacturers
Defense contractors and manufacturers working with sensitive military technologies face a critical question when selecting computer-aided design software: Is AutoCAD ITAR compliant? This question becomes

How to Get Help in Windows: Guide to Security and Compliance Support
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring your computer systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations is essential for both businesses and individuals. Windows, as one

Microsoft Copilot for GCC High: Enhancing Security and Compliance
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, organizations that handle sensitive data, particularly those in government sectors or defense contractors, face growing pressure to maintain strict security
Partner with Us for Compliance & Protection
We’re happy to answer any questions you may have and help you determine which of our services best fit your needs.
Your benefits:
- Client-oriented
- Security
- Compliance
- Peace of mind
- Efficiency
- Trust
What happens next?
Schedule an initial meeting
Arrange a discovery and assessment call
Tailor a proposal and solution
