Types of Penetration Testing: Which Better Suites Your Company?
Is your organization properly equipped to defend against the ever-increasing number of cyberattacks? Which cybersecurity measures have you put in place to ensure this? One of the best measures you can institute is to have regular penetration testing done against your information systems. Cybercriminals exploit unpatched vulnerabilities to launch sophisticated attacks against your organization’s IT infrastructure. In 2023 alone, there were 5119 critical vulnerabilities reported by security researchers. This would have been 5119 cases of cyberattacks against systems, underscoring the importance of pen testing. The cyberattacks have been increasing at an alarming rate The White House released a memo urging businesses to defend against ransomware through pen testing. For security researchers to prevent, detect, respond to, and recover from cyberattacks successfully, they must view information systems and networks from a threat actor’s point of view. This includes conducting various pentests described in this article. But before then, what is penetration testing?
What is Pentesting?
A penetration test refers to a simulated cyber attack aimed at finding, investigating, and patching vulnerabilities within an organization’s information systems and security infrastructure. In a pentest, the ethical hacker uses the same TTPs (tactics, techniques, and procedures) a cybercriminal uses to simulate the attack against a company. This allows them to understand the robustness of the implemented security controls in withstanding different cyberattacks. Some organizations also use pen testing to measure their compliance status. This is a requirement for some organizations, like those in the health and payment industries. Depending on whether performed internally or externally, pentesting can simulate different attack vectors. The aim and results of every pentesting engagement is determined by the needs of the company being assessed. The cost of the penetration will depend on various factors, including the scope, type of pentest, and experience of the penetration tester. Below are the different types of penetration testing:
Why Penetration Testing Matters
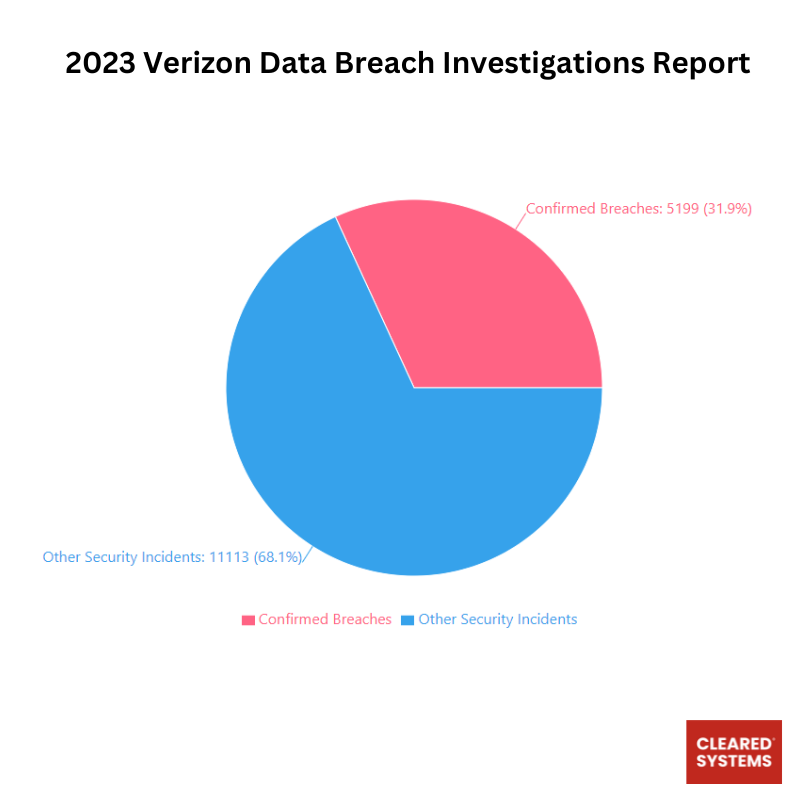
According to Verizon Data Breach report, out of 16,312 security incidents analyzed, 5,199 (31.9%) were confirmed as data breaches, while 11,113 (68.1%) were classified as other security incidents. A confirmed breach involves verified disclosure of data to an unauthorized party, whereas other security incidents may compromise information assets without confirmed data exposure. This data represents a sample of global incidents and highlights the significant proportion of security events that result in actual data breaches. Most of the incidents reported could have been prevented with regular penetration testing.
Types of Penetration Testing
There are several types of penetration tests, each with its unique approach and focus area. Understanding these types can help businesses decide which kind of test best suits their needs.
Mobile Application Pentesting
Pentesting mobile applications involves evaluating mobile apps and APIs they interact with, aiming to uncover any vulnerabilities. It also tests communications between a mobile application and servers. Mobile penetration testing also involves the analysis of the app’s binaries. Good mobile pentests include reverse engineering or decompiling the application’s souce code to collect as much information on its internals as possible. This can help a pentester obtain hardcoded key materials and secrets and bypass protections like certificate pinning and jailbreak detection through binary instrumentation.
Network Penetration Testing
This type of test focuses on identifying vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure. It assesses network components like routers, switches, and firewalls, aiming to exploit weaknesses in network protocols and services. The goal is to uncover any flaws that could allow unauthorized access or data breaches. Network penetration testing can reveal issues such as misconfigured network devices, weak or default passwords, and vulnerabilities in operating systems and applications. Network pentesting can be;
External Network Penetration Testing
The type of network penetration testing looks at your externally facing assets or publicly available information. The pentesting team tries to take advantage of the vulnerabilities found when screening public information. They also can try gaining access to data through externally facing assets like cloud-based applications, company emails, and websites.
Internal Network Penetration Testing
Internal network penetration testing starts where external pentesting ends. In this case, the pen tester simulates a malicious “insider,” like a disgruntled employee with legitimate access to the network. The aim of an internal network pentest is to role-play what can happen should a rogue contractor, cybercriminal, or employee masquerading as a member of an organization’s staff try to compromise the information systems from within. Penetration testers try to assess the repercussions of inadvertent disclosure, unauthorized alteration, misuse, or destruction of confidential information. They then use the findigs of this test to propose better controls for employees.
Network penetration testing helps your business from SSH, router, DNS-level, database, and zone transfer attacks. It is also instrumental in averting MiTM, SMTP/FTP, proxy server, routing/switching attacks, and IDS/IPS evasion.
Web Application Penetration Testing
Web app penetration testing is done to uncover vulnerabilities in websites, web applications, and other web services. This type of pen-testing uncovers vulnerabilities such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and command injections, among others. Through web application penetration testing, companies can test the exposed components such as firewalls, routers, and DNS servers and achieve compliance with standards and regulations such as HIPAA and GDPR.
Microservices and API Pentesting
API penetration is increasingly becoming popular because many companies are now using microservices and APIs to allow third parties to access their services and data. This type of penetration testing ensures GraphQL, web services, REST, and other kinds of APIs to enough security against known vulnerabilities. API and microservices testing aims to uncover vulnerabilities such as broken authentication, BOLA, unsafe API consumption, and unrestricted resource consumption. It also can help uncover secure misconfiguration, unrestricted access to sensitive data, and broken function level authorization vulnerabilities. Although API and microservices pentesting follow similar methods as application pentesting, specific considerations such as authorization and authentication mechanisms should be made. Other areas to consider include access control issues, rate limiting, and mass assignment.
Wireless Penetration Testing
“Wireless network penetration testing” focuses on assessing the security of Wi-Fi instead of exploring other wireless technologies. The primary objective of a wireless penetration test is to uncover and exploit security vulnerabilities within Wi-Fi, aiming to gain unauthorized access to a company’s network. It scrutinizes the adequacy of segregation between the wireless and corporate networks, potentially facilitating pivoting to sensitive servers. This thorough process uses diverse tools and techniques for scanning for wireless networks, identifying vulnerabilities, and simulating various attacks, including active ones like capturing and cracking WPA2 handshakes or passive approaches such as creating rogue access points to acquire wireless credentials. It can reveal issues such as weak encryption, insecure network configurations, and vulnerabilities like session reuse and de-authentication.
Social Engineering Testing
It is a matter of consensus within the security research community that humans are the weakest link in cybersecurity. Social engineering involves simulating attacks that exploit human psychology, such as phishing or baiting. The goal is to gauge the awareness and response of the organization’s staff to social engineering tactics. It helps organizations understand how susceptible their employees are to social engineering attacks and provides insights into areas where security awareness training may be needed.
Physical Penetration Testing
This test focuses on physical security measures. Testers attempt to breach security controls like locks, surveillance systems, and access controls to gain unauthorized access to physical locations. This type of testing can reveal vulnerabilities in an organization’s physical security measures, such as inadequate security of sensitive areas and poor access control procedures.
Client-Side Penetration Testing
This tests the security of client-side applications, such as web browsers and document readers, which can be exploited to gain access to an organization’s network. It can reveal vulnerabilities in client-side software that attackers could exploit to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or systems. Client-side testing helps identify vulnerabilities like HTML injection, open redirection, XSS, and CORS, among other attacks.
Cloud Penetration Testing
Cloud pentesting aims at identifying and exploiting security weaknesses in applications and infrastructure, hosted on cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure, to get unauthorized access to sensitive data. Cloud pen testing involves the use of different techniques and tools to scan for and identify misconfigurations and vulnerabilities in cloud-based assets. When contracting a vendor for a cloud pentest engagement, you must remember that this is not your typical network or application pentest. Cloud-hosted apps and infrastructure are often tested for security issues, but your penetration test provider must understand the specific cloud you use. For instance, an SSRF vulnerability in an AWS app can compromise the entire cloud infrastructure. Additionally, cloud services like AWS Cognito, Azure AD, RDS, and S3 buckets have their misconfigurations, so experienced pen testers are needed to recognize these services when found and leverage them in assessments.
Red Team Exercises
Red teaming is a sophisticated testing method inspired by military drills. It uses an aggressive strategy, putting an organization’s security protocols, procedures, and strategies to test. It merges physical, digital, and social aspects to mimic a thorough real-world attack situation, making it different from conventional penetration testing. Red teaming includes activities associated with various forms of penetration testing. While a regular pentest seeks to uncover as many vulnerabilities as it can within a specified period, it is often constrained by artificial limitations like the scope of the task.
Although routine penetration tests are crucial, they lack realistic conditions, such as integrated attack methods. Red teaming enables security teams to evaluate the entire environment and understand how its elements work in unison. However, it requires critical thinking to discover new, intricate vulnerabilities. Red team pen tests generally take longer than standard penetration tests and often require several months to finish. This intricate nature makes red teaming not as frequent and only possible for large organizations.
IoT Penetration Testing
This type focuses on the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, such as smart appliances, industrial systems, or healthcare equipment. It aims to discover vulnerabilities that could be exploited in these increasingly connected devices. It can help organizations identify and address security weaknesses in their IoT devices, reducing the risk of attacks that could lead to data breaches or other security incidents.
Teams in Penetration Testing and Their Roles
Penetration testing is not a one-size-fits-all process and often involves different teams with specialized skills and objectives. Understanding these teams and their roles can provide insight into how comprehensive penetration testing is conducted.
Red Team
The primary goal of the Red Team is to simulate the tactics, techniques, and procedures of real-world attackers. They actively attempt to compromise systems, breach defenses, and exploit vulnerabilities in an organization’s security. Red teamers’ activities include advanced penetration testing, social engineering, physical breach attempts, and custom exploit development. They operate under a ‘no-holds-barred’ approach, mimicking an actual adversary.
Blue Team
In contrast to the Red Team, the Blue Team is responsible for defending against attacks and focuses on improving the organization’s defenses and responding to incidents. The Blue Team’s tasks include monitoring and securing networks, implementing security policies, conducting regular vulnerability assessments, and responding to breaches. They are essentially the organization’s internal cybersecurity team.
Purple Team
The Purple Team bridges the gap between the Red and Blue teams. Their objective is to maximize the effectiveness of both teams by facilitating communication and collaboration. A purple team works by ensuring the Red Team’s findings are effectively communicated and understood by the Blue Team and that appropriate defensive measures are implemented. The Purple Team helps translate attack scenarios into defensive strategies and vice versa.
White Team
Often seen in controlled environments like cyber range exercises or capture-the-flag (CTF) events, the White Team oversees and manages these exercises. They are responsible for setting objectives, rules of engagement, scoring, and ensuring that the exercises are conducted fairly and effectively. A White team acts as referee, ensuring that both Red and Blue Teams adhere to the agreed parameters.
Green Team
The Green Team is focused on the organization’s IT and network infrastructure. They maintain and support the systems and networks that the Red and Blue Teams use during testing. A green team is responsible for ensuring that the testing environment is stable, secure, and reflective of real-world systems.
Black Team
This team is less commonly referenced and typically involves specialists who focus on physical security. Black teams assess and improve physical security measures like surveillance systems, access controls, and building security protocols.
Gold Team
The Gold Team consists of stakeholders and decision-makers, such as senior management or executives. They define the overall objectives, scope, and goals of the penetration testing. The Gold Team is responsible for making strategic decisions based on the outcomes of the testing and ensuring that the results align with the organization’s broader objectives.
Conclusion
A well-rounded security strategy may involve multiple types of penetration tests to ensure comprehensive coverage of all potential vulnerabilities. By regularly conducting penetration tests, organizations can stay ahead of emerging threats and strengthen their overall security posture. However, there are different pentesting teams, with each team playing a crucial role in ensuring a comprehensive and effective penetration testing process. Their collaboration and distinct focuses contribute to a robust security posture, enabling organizations to identify vulnerabilities and strengthen their defenses against potential cyber threats. It’s important to remember that penetration testing is not a one-time activity but a continuous process of identifying, addressing, and monitoring security vulnerabilities.
For a thorough and professional penetration testing experience, consider partnering with Cleared Systems, your trusted cybersecurity ally. Our expert teams are equipped to handle all your penetration testing needs, ensuring your organization’s resilience against evolving threats. Stay secure, stay protected – partner with us for proactive cybersecurity measures. Contact us today to fortify your defenses!
Share in Social Media
See More Case Studies

Securing Defense Contracts: A DFARS 252.204-7012 Compliance Case Study
Discover how Cleared Systems helped a Federal Contractor successfully achieve DFARS 252.204-7012 compliance by strengthening its cybersecurity posture, giving it a competitive edge when bidding for DoD Contracts.

What is GCC High? For ITAR & CMMC 2.0
Microsoft 365 Government Community Cloud (GCC) High is a specialized cloud solution tailored for U.S. federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations, as well as for contractors who hold or process data subject to specific security regulations. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, and differences between Microsoft 365 GCC High and other Office 365 offerings.
Is AutoCAD ITAR Compliant? A Comprehensive Guide for Defense Manufacturers
Defense contractors and manufacturers working with sensitive military technologies face a critical question when selecting computer-aided design software: Is AutoCAD ITAR compliant? This question becomes

How to Get Help in Windows: Guide to Security and Compliance Support
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring your computer systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations is essential for both businesses and individuals. Windows, as one

Microsoft Copilot for GCC High: Enhancing Security and Compliance
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, organizations that handle sensitive data, particularly those in government sectors or defense contractors, face growing pressure to maintain strict security
Partner with Us for Compliance & Protection
We’re happy to answer any questions you may have and help you determine which of our services best fit your needs.
Your benefits:
- Client-oriented
- Security
- Compliance
- Peace of mind
- Efficiency
- Trust
What happens next?
Schedule an initial meeting
Arrange a discovery and assessment call
Tailor a proposal and solution
