How to Manage ITAR and EAR Export Compliance Program
In today’s globalized business environment, managing an effective export compliance program is crucial for companies dealing with sensitive technologies, defense articles, and controlled information. Two primary regulatory frameworks govern U.S. export controls: the International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) and the Export Administration Regulations (EAR). This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential steps to create, implement, and maintain a robust export compliance program that adheres to both ITAR and EAR requirements.
Understanding ITAR and EAR
What is ITAR?
The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) is a set of U.S. government regulations that control the export and import of defense-related articles and services on the United States Munitions List (USML). ITAR is administered by the U.S. Department of State’s Directorate of Defense Trade Controls (DDTC).
According to the U.S. Department of State:
“The International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR) is the set of regulations that control the export of defense-related articles and services on the United States Munitions List (USML).”
What is EAR?
The Export Administration Regulations (EAR) are a set of regulations administered by the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS). These regulations govern the export of commercial and dual-use items, which are items that have both commercial and military applications.
The Bureau of Industry and Security states:
“The Export Administration Regulations (EAR) are issued by the United States Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) under laws relating to the control of certain exports, reexports, and activities.”
Struggling to Manage ITAR and EAR Compliance?
Key Components of an Export Compliance Program
1. Management Commitment
A successful export compliance program starts at the top. Senior management must demonstrate a clear commitment to compliance and allocate necessary resources to support the program.
Implementing Management Commitment
- Develop a written export compliance policy signed by the CEO or President
- Appoint a senior executive as the Export Compliance Officer
- Allocate sufficient budget and resources for the compliance program
2. Risk Assessment
Conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential export compliance vulnerabilities within your organization.
Performing a Risk Assessment
- Analyze your products, technologies, and services against ITAR and EAR regulations
- Evaluate your customer base and international business activities
- Assess your internal processes and controls
3. Export Compliance Manual
Develop a comprehensive export compliance manual that outlines your company’s policies and procedures for adhering to ITAR and EAR regulations.
Key Elements of an Export Compliance Manual
- Overview of ITAR and EAR regulations
- Product classification procedures
- Licensing requirements and procedures
- Screening processes for restricted parties
- Record-keeping guidelines
- Internal audit procedures
- Training requirements
4. Training and Awareness
Implement a robust training program to ensure all employees understand their roles and responsibilities in maintaining export compliance.
Designing an Effective Training Program
- Develop role-specific training modules
- Conduct regular refresher courses
- Maintain training records
- Establish a system for communicating regulatory updates
The Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) emphasizes the importance of training:
“OFAC encourages companies to take a risk-based approach to sanctions compliance by developing, implementing, and routinely updating a sanctions compliance program (SCP). An effective SCP generally consists of five essential components: (1) management commitment; (2) risk assessment; (3) internal controls; (4) testing and auditing; and (5) training.”
5. Recordkeeping
Maintain accurate and detailed records of all export-related activities to ensure compliance and facilitate audits.
Essential Recordkeeping Practices
- Establish a centralized system for storing export-related documents
- Implement retention policies in line with ITAR and EAR requirements
- Regularly backup and secure sensitive information
- Develop procedures for retrieving records during audits or investigations
6. Auditing and Monitoring
Conduct regular internal audits to assess the effectiveness of your export compliance program and identify areas for improvement.
Implementing an Effective Audit Program
- Develop an audit schedule and checklist
- Perform both routine and surprise audits
- Document audit findings and corrective actions
- Report audit results to senior management
7. Handling Violations and Voluntary Disclosures
Establish procedures for identifying, investigating, and reporting potential export violations.
Managing Export Violations
- Develop a process for employees to report suspected violations
- Implement a protocol for investigating potential violations
- Understand the voluntary disclosure processes for both ITAR and EAR
- Seek legal counsel when necessary
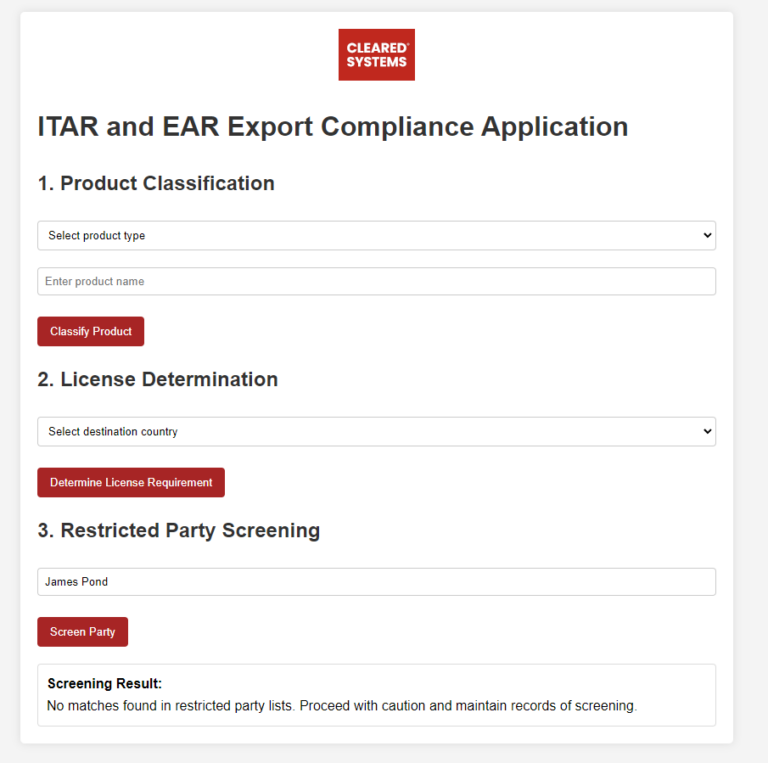
ITAR-Specific Compliance Considerations
Registration Requirements
Companies that manufacture, export, or temporarily import defense articles or furnish defense services must register with the DDTC.
ITAR Registration Process
- Submit Form DS-2032 and required documentation
- Pay the registration fee
- Renew registration annually
Technical Data Control
ITAR places strict controls on the export of technical data related to defense articles.
Managing Technical Data under ITAR
- Implement access controls for ITAR-controlled technical data
- Develop procedures for sharing technical data with foreign persons
- Train employees on the proper handling of ITAR-controlled information
The U.S. Department of State provides guidance on technical data:
“Technical data is information required for the design, development, production, manufacture, assembly, operation, repair, testing, maintenance or modification of defense articles. This includes information in the form of blueprints, drawings, photographs, plans, instructions or documentation.”
EAR-Specific Compliance Considerations
Product Classification
Proper classification of items under the Commerce Control List (CCL) is crucial for EAR compliance.
Steps for Product Classification
- Review the CCL to determine the Export Control Classification Number (ECCN)
- Identify reasons for control and applicable license exceptions
- Document the classification process and rationale
Deemed Exports
Under EAR, the release of controlled technology or source code to a foreign person within the U.S. is considered a deemed export.
Managing Deemed Exports
- Implement procedures to identify and control deemed exports
- Obtain necessary licenses for technology transfers to foreign nationals
- Train employees on deemed export requirements
Leveraging Technology for Export Compliance
In today’s digital age, leveraging technology can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your export compliance program.
Compliance Management Software
Invest in specialized export compliance software to streamline processes and reduce human error.
Benefits of Compliance Software
- Automated screening against restricted party lists
- Centralized document management
- Real-time regulatory updates
- Automated license determination and application
Blockchain for Secure Record-keeping
Explore the potential of blockchain technology for maintaining tamper-proof export compliance records.
Advantages of Blockchain in Export Compliance
- Immutable audit trail
- Enhanced security and transparency
- Improved traceability of exported items
Staying Current with Regulatory Changes
Export regulations are subject to frequent updates. Staying informed about these changes is crucial for maintaining compliance.
Strategies for Keeping Up-to-Date
- Subscribe to official government newsletters and alerts
- Attend industry conferences and webinars
- Join professional associations focused on export compliance
- Regularly review the websites of relevant government agencies
The Export Control and Related Border Security (EXBS) Program emphasizes the importance of staying current:
“The EXBS Program is the United States Government’s premier initiative to help other countries improve their export control systems. The EXBS Program takes a comprehensive approach to export control reform that includes laws, regulations, and procedures for enforcement, licensing, industry compliance, and interagency coordination.”
Building a Culture of Compliance
Creating a culture of compliance is essential for the long-term success of your export compliance program.
Fostering a Compliance-Oriented Culture
- Lead by example – ensure management visibly supports compliance efforts
- Integrate compliance considerations into business decision-making processes
- Recognize and reward employees for compliance achievements
- Encourage open communication about compliance concerns
Challenges in Managing an Export Compliance Program
Implementing and maintaining an effective export compliance program comes with its share of challenges.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Resource Constraints
- Solution: Prioritize high-risk areas and leverage technology to increase efficiency
- Rapidly Changing Regulations
- Solution: Implement a system for monitoring and disseminating regulatory updates
- Global Supply Chain Complexity
- Solution: Develop clear procedures for vetting and monitoring international partners
- Balancing Compliance with Business Objectives
- Solution: Integrate compliance considerations into strategic planning processes
Measuring the Effectiveness of Your Export Compliance Program
Regularly assessing the performance of your export compliance program is crucial for continuous improvement.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Export Compliance
- Number of successful license applications
- Time to obtain export licenses
- Number of compliance violations identified and resolved
- Employee training completion rates
- Results of internal and external audits
Conclusion
Managing an effective ITAR and EAR export compliance program requires dedication, resources, and ongoing attention. By implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can build a robust compliance framework that protects your organization from regulatory violations while supporting your international business objectives.
Remember that export compliance is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process. Regularly review and update your program to ensure it remains effective in the face of changing regulations and business environments.
Are you looking to enhance your organization’s export compliance program? Cleared Systems offers comprehensive solutions tailored to your specific needs. Our team of experts can help you navigate the complexities of ITAR and EAR regulations, implement cutting-edge compliance technologies, and build a culture of compliance within your organization.
Don’t leave your export compliance to chance. Contact Cleared Systems today for a free consultation and take the first step towards a more secure and efficient export compliance program.
Share in Social Media
See More Case Studies

Securing Defense Contracts: A DFARS 252.204-7012 Compliance Case Study
Discover how Cleared Systems helped a Federal Contractor successfully achieve DFARS 252.204-7012 compliance by strengthening its cybersecurity posture, giving it a competitive edge when bidding for DoD Contracts.

What is GCC High? For ITAR & CMMC 2.0
Microsoft 365 Government Community Cloud (GCC) High is a specialized cloud solution tailored for U.S. federal, state, local, tribal, and territorial government organizations, as well as for contractors who hold or process data subject to specific security regulations. In this article, we will explore the features, benefits, and differences between Microsoft 365 GCC High and other Office 365 offerings.
Is AutoCAD ITAR Compliant? A Comprehensive Guide for Defense Manufacturers
Defense contractors and manufacturers working with sensitive military technologies face a critical question when selecting computer-aided design software: Is AutoCAD ITAR compliant? This question becomes

How to Get Help in Windows: Guide to Security and Compliance Support
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring your computer systems are secure and compliant with industry regulations is essential for both businesses and individuals. Windows, as one

Microsoft Copilot for GCC High: Enhancing Security and Compliance
In today’s fast-evolving digital landscape, organizations that handle sensitive data, particularly those in government sectors or defense contractors, face growing pressure to maintain strict security
Partner with Us for Compliance & Protection
We’re happy to answer any questions you may have and help you determine which of our services best fit your needs.
Your benefits:
- Client-oriented
- Security
- Compliance
- Peace of mind
- Efficiency
- Trust
What happens next?
Schedule an initial meeting
Arrange a discovery and assessment call
Tailor a proposal and solution
